
View the complete article here.
Hoisting loads with a wire rope is a simple operation. Hook it up; lift it. Turns out, it’s more complicated than it appears. The details of setting up, inspecting, and maintaining lifts with wire ropes are not complicated, but are critical. A lift that goes awry is dangerous. A bad lift puts workers at risk. In this article, we discuss the causes of wire rope failure and how to avoid them.
Types of Rope Wire Damage
A wire rope is subject to several types of damage, including:
Abrasion Breaks
Abrasion breaks are caused by external factors such as coming into contact with improperly grooved sheaves and drums. Or just hitting against some object during operation. Worn, broken wire ends is the result of an abrasion break. Common causes of abrasion breaks include:
- An improperly sized rope
- Poor spooling
- Grooves that are too tight
- Sheaves that are misaligned
- Sheaves or rollers that are frozen
- Excessive fleet angle
Core Slippage or Protrusion
Core slippage or protrusion is caused by shock load or improper installation of the wire rope. Excessive torque can cause core slippage that forces the outer strands to shorten. The core will then protrude from the rope. Wire ropes designed to be rotation-resistant should be handled carefully so as not to disturb its lay length.
Corrosion Breaks
Corrosion breaks cause pitting on the individual wires that comprise the rope. This type of damage is caused by poor lubrication. However, corrosion breaks are also caused by the wire rope coming into contact with corrosive chemicals, such as acid.
Crushing
There are many ways the strands of a rope can be crushed or flattened. Improper installation is a common cause. To avoid crushing, you’ll want the first layer of the wire rope to be very tight. You’ll also need to properly break-in a new wire rope. Other causes of crushing include cross winding, using a rope of the wrong diameter, or one that it too long.
Fatigue Breaks
Cracks to individual wires are caused by fatigue breaks. Fatigue breaks happen because the wire rope is being bent over the sheave over and over again. In time, the constant rubbing of the wire rope against the sheave or drum causes these breaks. Sheaves that are too small will accelerate fatigue breaks because they require more bending. Worn bearings and misaligned sheaves can also cause fatigue. A certain number of broken wires is acceptable. The worker responsible for equipment inspection prior to use should know the American Society of Mechanical Engineers (ASME) standard for wire ropes. The ASME standard determines whether the wire rope must be replaced. (https://www.asme.org/)
Other types of damage include looped wires, lay lengthening, and kinking.
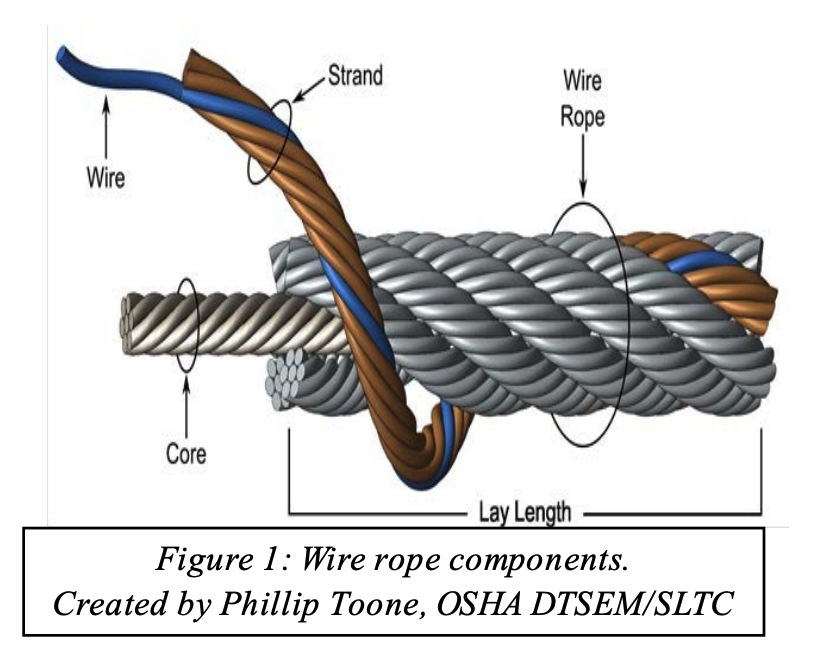
Tips for Avoiding Rope Failures
There are specific steps you can take to prevent wire rope failures.
Selecting the Right Wire Rope
Selecting the right wire rope for the job is critical. There is never a perfect rope. For example, you will need to make a tradeoff between fatigue resistance and abrasion resistance. There are several aspects to wire rope design to consider, including:
- Fatigue Resistance
- Abrasion Resistance
- Strength
- Crushing Resistance
- Rotation Resistance
- Metal Loss and Deformation Resistance
In general, the proper wire rope will have a strength rating high enough to handle the load. (Strength is rated in tons.) It can handle the stress of repeated bending as it passes over sheaves or around drums. How you attach the rope in preparation for the lift matters and should only be handled by properly trained workers.
Inspection and Maintenance
The wire rope (and all the equipment involved in a lift) should be fully inspected prior to the lift. The worker performing the inspection should be well-versed in the types of damage that can cause a wire rope to fail. Using a checklist is highly recommended. This will ensure that the inspection is complete. Worker and supervisor signoff will increase accountability. Of course, the wire rope must be maintained according to the manufacturer’s instructions.
Environmental Effects on Wire Ropes
How a wire rope is stored, the weather conditions in which it is used, and how they are cleaned all affect its useful life. The Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) provides these recommendations: (Source: https://www.osha.gov/dsg/guidance/slings/wire.html)
- Do not store wire ropes in extreme temperatures. The manufacturer or qualified worker can provide guidance on using them in extreme temperatures.
- Store them in a dry area.
- Keep them away from corrosive materials.
- Do not use a degreasing or other corrosive solvent to clean fiber-core wire rope.
- Always follow the manufacturer’s recommendations for lubrication of the wire rope.
Rigging Practices
You should follow the rigging practices outlined by OSHA which include:
- Hitch slings in a way that allows you to control the load.
- Protect the sling with sufficient padding to avoid damage from sharp edges.
- Only adjust the size of the sling by a method approved by the manufacturer or qualified worker.
- Ensure that workers are on the ready to deal with possible snagging.
- To prevent slippage in a basket hitch, balance the load and support it from the sides (above the center of gravity).
- For a choker hitch, the choke points should only be on the sling body and not on a fitting. Also, reduce the rated load when an angle of a choke is under 120 degrees.
- A sling should not be bunched up or constricted in any way. Nor should it be pinched by any fitting, hook, or the load itself.
- Where a hook is not designed for point loading, ensure the load that is applied to the hook is centered in the base of the hook.
- An object in the eye of the sling should not exceed 50% of the length of the eye.
For the complete list of rigging practices: https://www.osha.gov/dsg/guidance/slings/wire.html
Conclusion
Preventing wire rope failures starts with selecting the right one for the job. When in doubt, talk with your local equipment dealer. Be prepared to discuss your specific job requirements. A thorough inspection of the wire rope prior to using it is critical. Finally, properly store your wire rope. The selection, inspection, and care of wire rope is key to job safety.
View the complete article here.
How can I prevent wire rope failures, and what are the common types of wire rope damage?
To prevent wire rope failures, select the right type considering factors like fatigue and abrasion resistance, conduct regular inspections, and follow proper storage and maintenance practices. Common types of damage include abrasion breaks, core slippage, corrosion breaks, crushing, and fatigue breaks.
What environmental factors affect wire rope life, and what rigging practices should be followed to ensure safety?
Environmental factors affecting wire rope include storage conditions, weather, and cleaning methods. Rigging practices should align with OSHA guidelines, emphasizing proper load control, padding, sling adjustment, and avoiding sling constriction for safety.














































